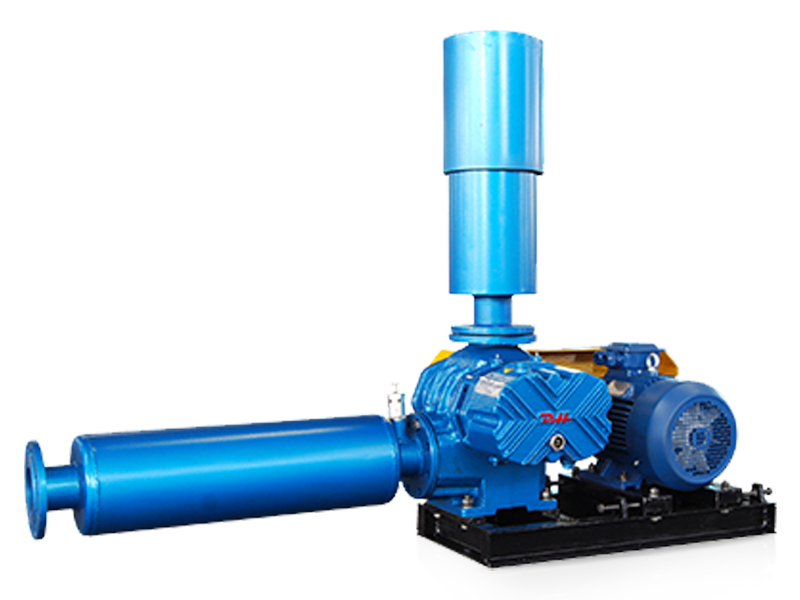
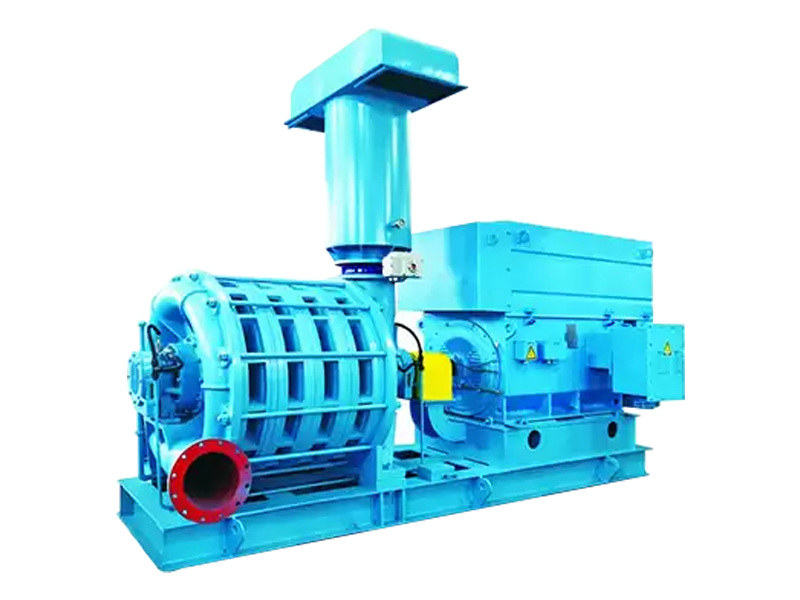
Understanding Systems Combined with Roots Blowers
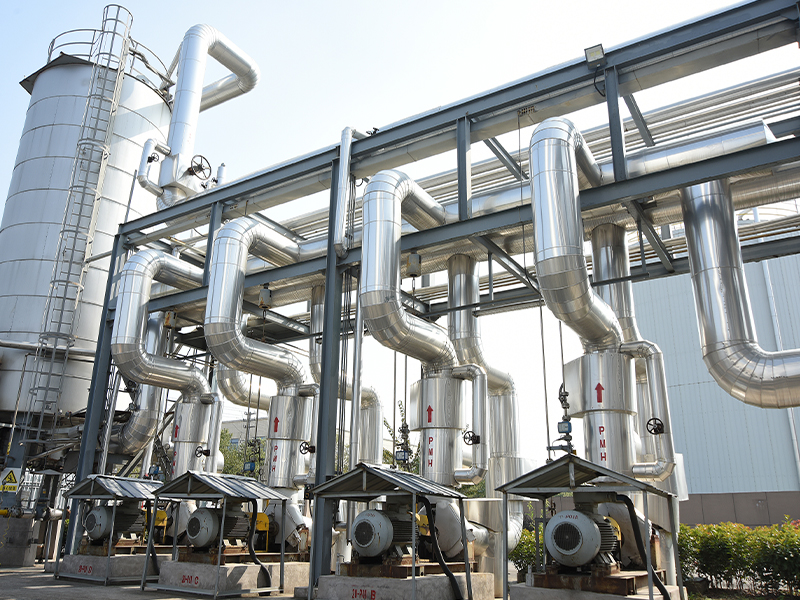
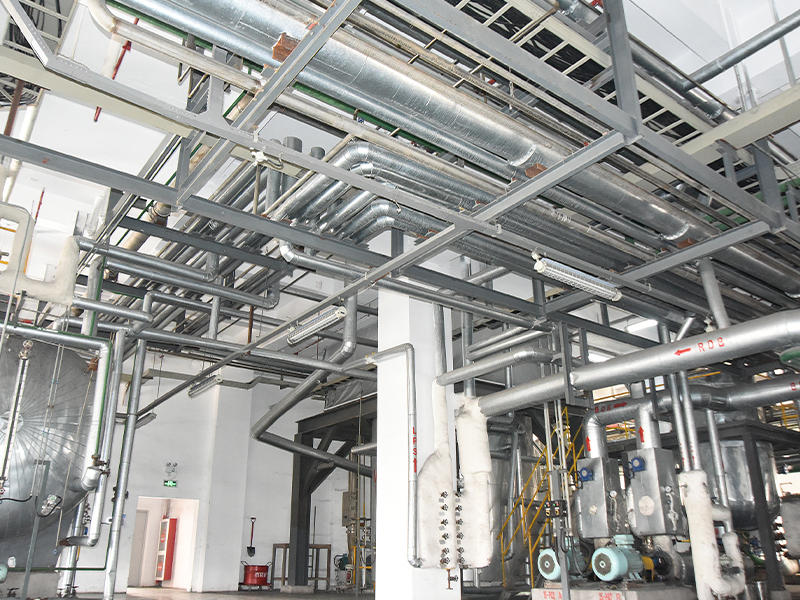
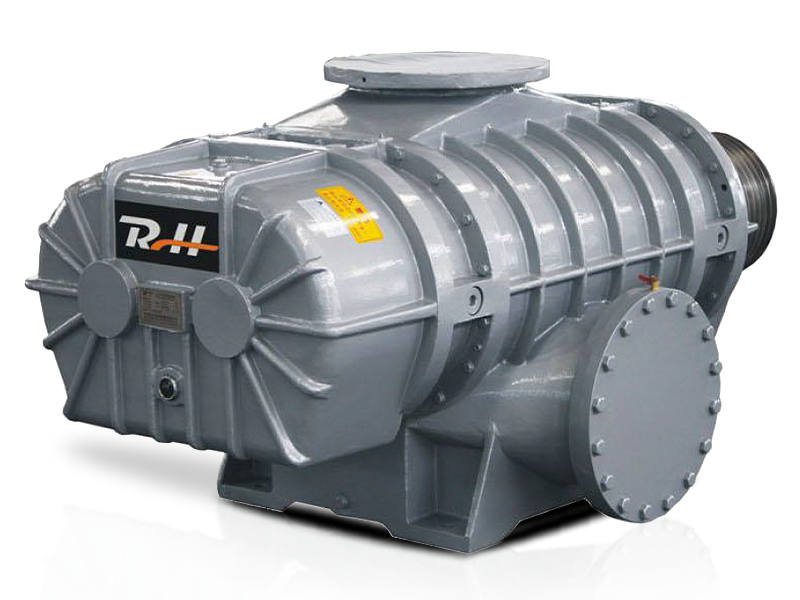
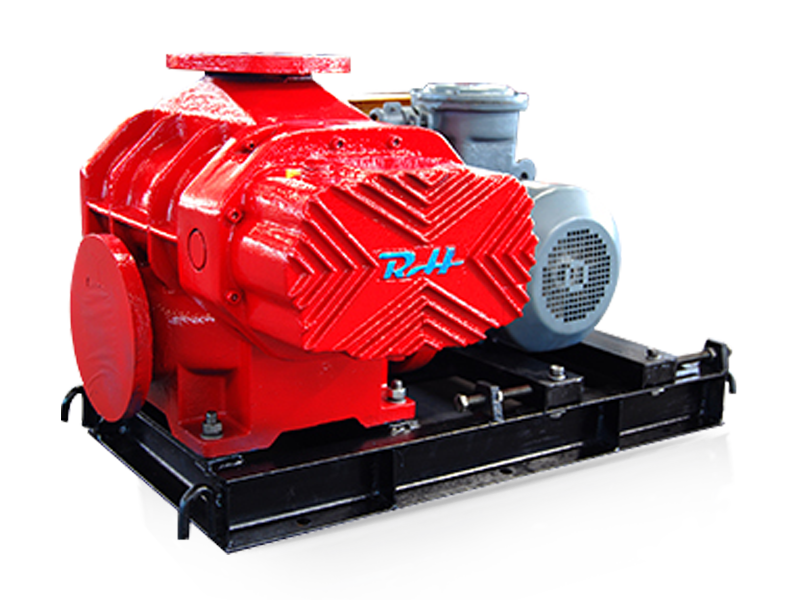
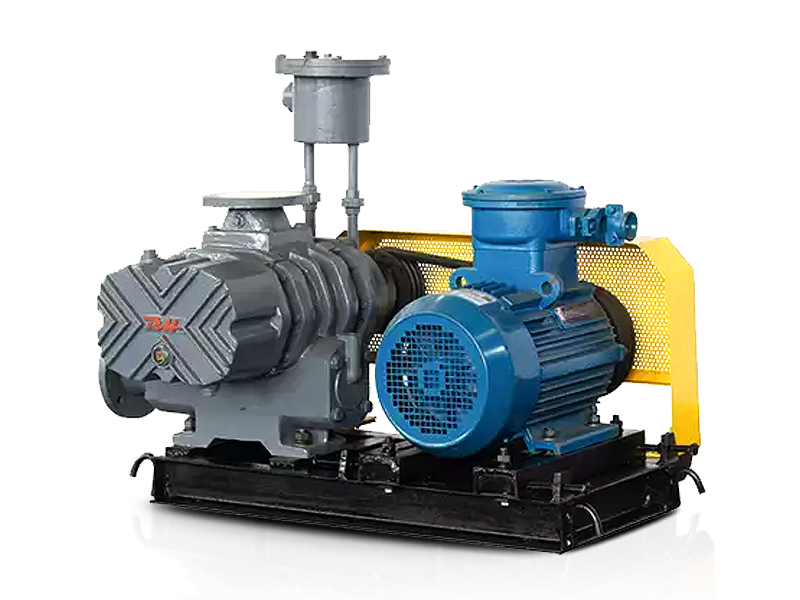
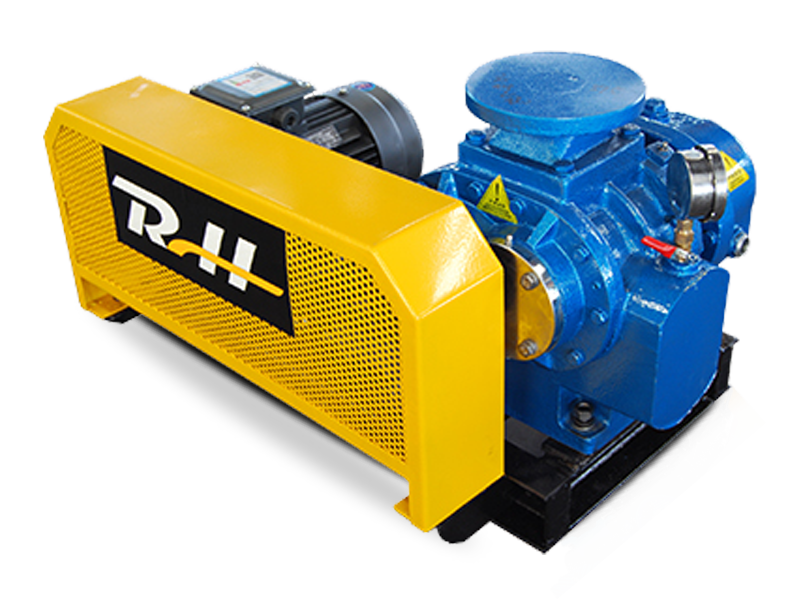
Roots blowers are positive displacement machines designed to move air or gas at a constant flow rate. When combined with supporting systems such as motors, silencers, filters, piping, and control units, they become complete Roots blower systems capable of handling demanding industrial tasks. These integrated setups are widely used in wastewater treatment, pneumatic conveying, cement plants, power generation, and chemical processing where stable airflow and pressure are required.
A Roots blower on its own provides displacement, but the surrounding system determines efficiency, reliability, and operating cost. Understanding how Roots blowers are combined with other components helps engineers and operators optimize performance while minimizing downtime and energy consumption.
Core Components in a Roots Blower System
A complete Roots blower system is built by integrating multiple mechanical and electrical components. Each element has a direct influence on airflow stability, noise control, and equipment life. Proper selection ensures the blower operates within its design limits.
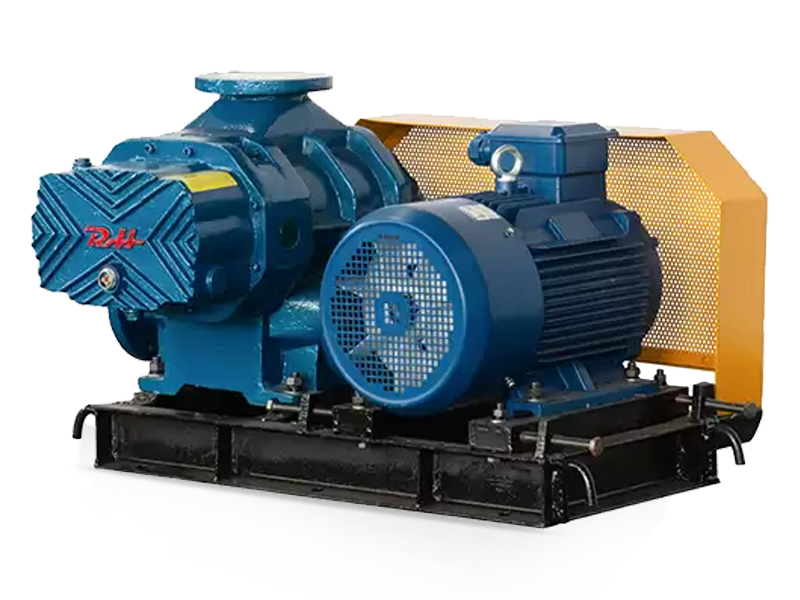
- Drive motor: Supplies stable power and is matched to blower capacity and pressure requirements.
- Inlet filter and silencer: Removes dust and reduces intake noise, protecting internal rotors.
- Discharge silencer: Lowers pulsation noise caused by positive displacement airflow.
- Pressure relief valve: Prevents overpressure damage during abnormal operating conditions.
- Base frame and coupling: Ensures alignment and reduces vibration during long-term operation.
Industrial Applications Combined with Roots Blowers
Roots blowers are rarely used alone in industrial environments. They are typically combined with process-specific systems to meet operational needs. These combinations provide reliable air or gas flow regardless of pressure fluctuations.
Wastewater Treatment Aeration Systems
In wastewater treatment plants, Roots blowers are combined with aeration piping, diffusers, and automated control panels. The blower supplies oxygen to biological treatment tanks, supporting microbial activity. Stable airflow improves treatment efficiency and reduces energy waste compared to unstable air sources.
Pneumatic Conveying Systems
For pneumatic conveying, Roots blowers are integrated with pipelines, rotary valves, and material separators. This combination allows powders, grains, and pellets to be transported over long distances. Roots blowers are preferred because they maintain consistent flow even as system resistance changes.
Vacuum and Gas Boosting Applications
When combined with vacuum piping and condensate separation systems, Roots blowers can function as Roots vacuum pumps or gas boosters. These setups are common in chemical processing, packaging, and power plants where low-pressure gas handling is required.
Performance Benefits of Combined Roots Blower Systems
Using Roots blowers as part of a complete system offers measurable performance benefits. Integration allows airflow, pressure, and energy consumption to be controlled more precisely than standalone equipment.
- Constant volumetric flow regardless of pressure variations.
- Improved energy efficiency when paired with variable frequency drives.
- Reduced system noise through combined inlet and outlet silencing.
- Enhanced equipment lifespan due to stable operating conditions.
Comparison of Common Roots Blower System Configurations
Different industries combine Roots blowers with different system layouts. The table below highlights typical configurations and their practical use cases.
| System Type | Combined Components | Typical Application |
| Aeration System | Blower, diffuser, piping, controls | Wastewater treatment |
| Conveying System | Blower, pipeline, feeder | Powder and bulk transport |
| Vacuum System | Blower, separator, vacuum piping | Packaging and gas recovery |
Maintenance Considerations for Integrated Roots Blower Systems
Maintenance of Roots blowers combined with other equipment requires a system-level approach. Regular inspection of only the blower is not sufficient, as supporting components influence operating conditions.
Operators should monitor inlet filter cleanliness, belt or coupling alignment, lubrication intervals, and pressure readings across the entire system. A clogged filter or blocked pipeline can increase load on the blower and reduce efficiency.
Design Tips When Combining Roots Blowers with Other Systems
Effective system design starts with accurate airflow and pressure calculations. Oversizing or undersizing the blower leads to unnecessary energy consumption or unstable operation. Designers should consider future expansion, ambient conditions, and operating hours when specifying equipment.
Using properly sized silencers, flexible connectors, and control instrumentation ensures the combined Roots blower system operates smoothly and meets environmental and safety requirements.
Conclusion: Practical Value of Roots Blowers Combined with Systems
Roots blowers deliver their full value when combined with well-designed systems tailored to specific industrial processes. From wastewater aeration to pneumatic conveying and vacuum boosting, integrated Roots blower systems provide consistent airflow, operational stability, and long service life. Focusing on proper component selection, system layout, and maintenance practices helps organizations achieve reliable performance and lower operating costs.


 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى