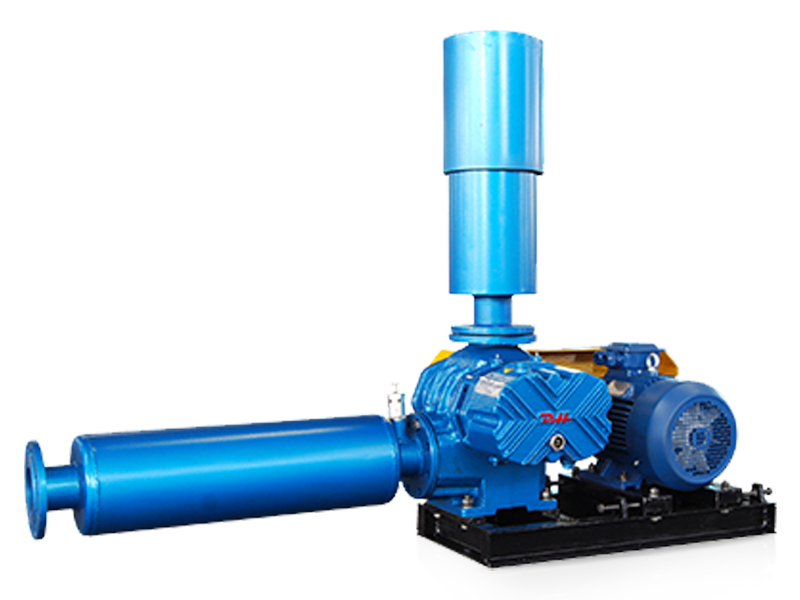
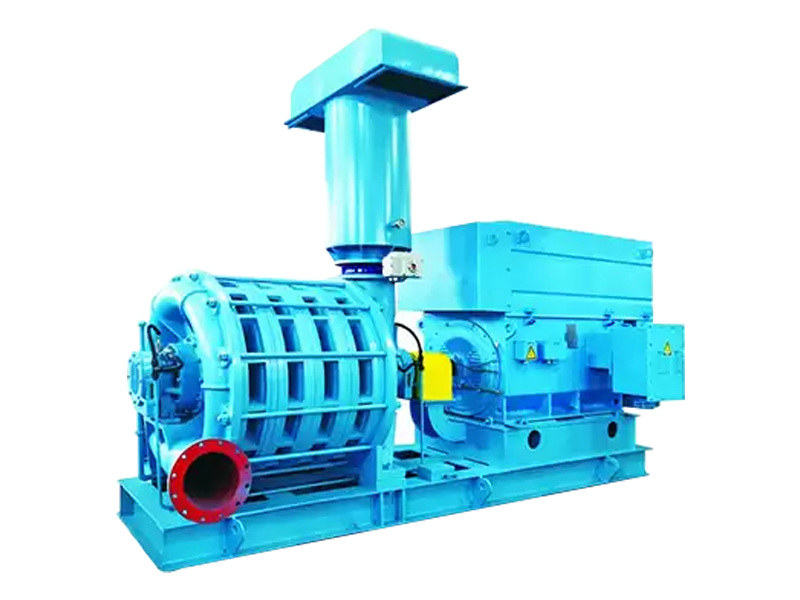
Understanding Roots Blowers and Their Industrial Role
Roots blowers, also known as rotary lobe blowers, are positive displacement machines widely used in industries for air and gas transfer. They operate by trapping a fixed volume of air or gas and transferring it from the inlet to the outlet. Their simple design, reliability, and capability to handle large volumes of air at relatively low pressures make them ideal for applications such as wastewater treatment, pneumatic conveying, and combustion air supply in boilers. Understanding their operation principles is crucial for selecting the right blower for specific industrial needs.
Core Components and Operating Principle
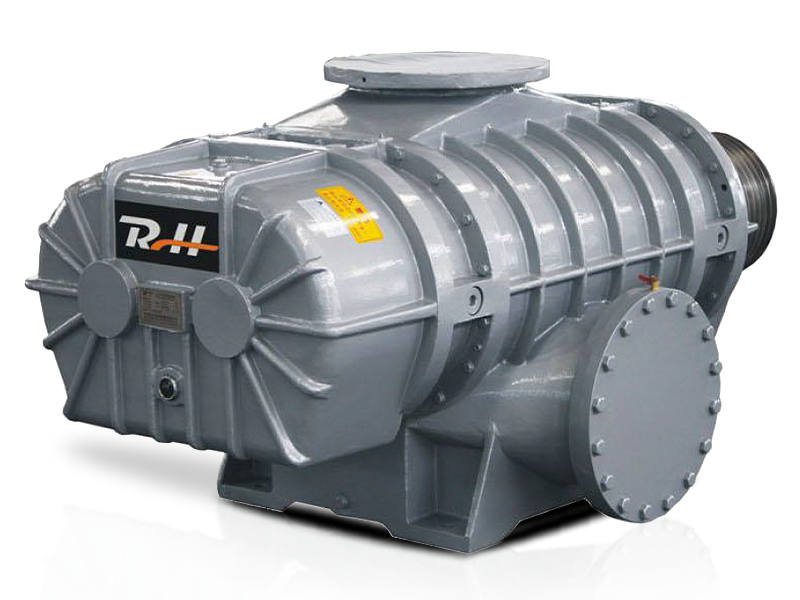
A typical Roots blower consists of two counter-rotating lobes enclosed in a casing. The lobes do not touch each other but rotate synchronously using timing gears. As the lobes rotate, air is trapped between the lobes and the casing, moving from the inlet side to the outlet side. This process generates a steady, pulsation-free airflow with minimal heat generation. Because they are positive displacement devices, Roots blowers can maintain consistent flow rates regardless of downstream pressure variations, making them reliable for continuous industrial processes.
Lobe Design Variations
Roots blower lobes can have different shapes—single-lobe, twin-lobe, or tri-lobe designs. Twin-lobe configurations are most common for general industrial use due to their balance of airflow efficiency and mechanical simplicity. Tri-lobe designs provide smoother airflow with reduced pulsations, which is particularly useful in sensitive pneumatic conveying systems. Selecting the correct lobe type depends on the required airflow, pressure, and noise reduction needs.
Industrial Applications of Roots Blowers
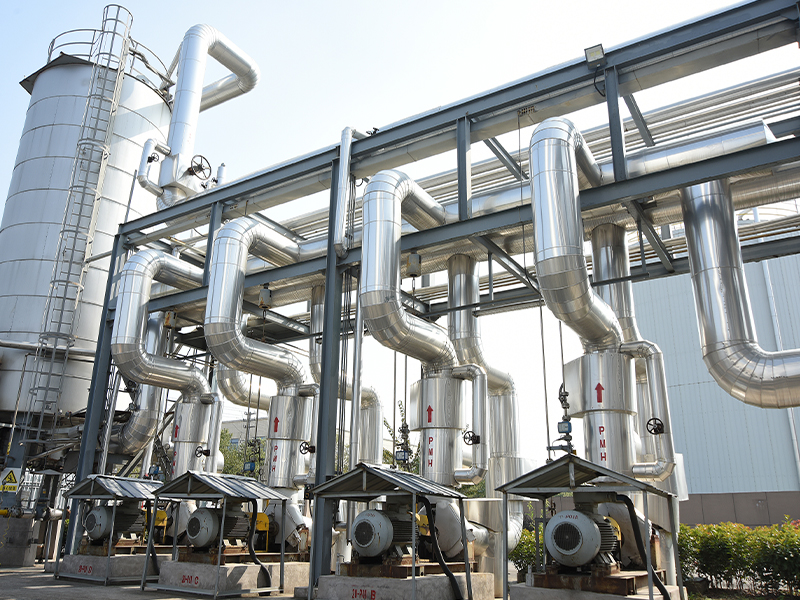
Roots blowers are highly versatile and find applications across multiple industries due to their reliability and high efficiency. They are commonly used in wastewater treatment plants to supply aeration for biological processes. In chemical and petrochemical industries, they provide air for oxidation and combustion processes. Pneumatic conveying systems use Roots blowers to transport granular or powdered materials efficiently over long distances. Additionally, they serve as vacuum pumps in packaging and food processing applications.
Wastewater Treatment
Aeration in wastewater treatment requires a steady supply of oxygen to support microbial activity that breaks down organic waste. Roots blowers deliver large volumes of air at controlled pressures to diffusers submerged in the treatment tanks. Their ability to maintain a consistent airflow ensures optimal biological performance and energy efficiency.
Pneumatic Conveying
In bulk material handling, Roots blowers generate the necessary airflow to move powders, grains, or pellets through pipelines. They offer a balance between sufficient pressure and minimal material degradation. Their positive displacement nature allows for precise control of material transport speed, which is crucial in industries like cement, food, and plastics.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips
Proper maintenance of Roots blowers is essential to ensure long-term efficiency and avoid costly downtime. Key maintenance tasks include regular lubrication of bearings and timing gears, monitoring for abnormal vibrations or noise, and checking for air leaks in the inlet and outlet connections. Timing gear alignment must be inspected periodically to prevent lobe contact, which can cause severe damage. Keeping filters clean ensures that contaminants do not enter the blower, extending its operational life.
Common Troubleshooting Scenarios
Roots blowers may experience issues such as reduced airflow, unusual vibration, or overheating. Reduced airflow can indicate clogged filters or pipe obstructions, while excessive vibration often points to misaligned timing gears or worn bearings. Overheating is typically caused by insufficient lubrication or operating at pressures beyond the blower's design limits. Timely identification and resolution of these issues prevent damage and maintain operational efficiency.
Selecting the Right Roots Blower
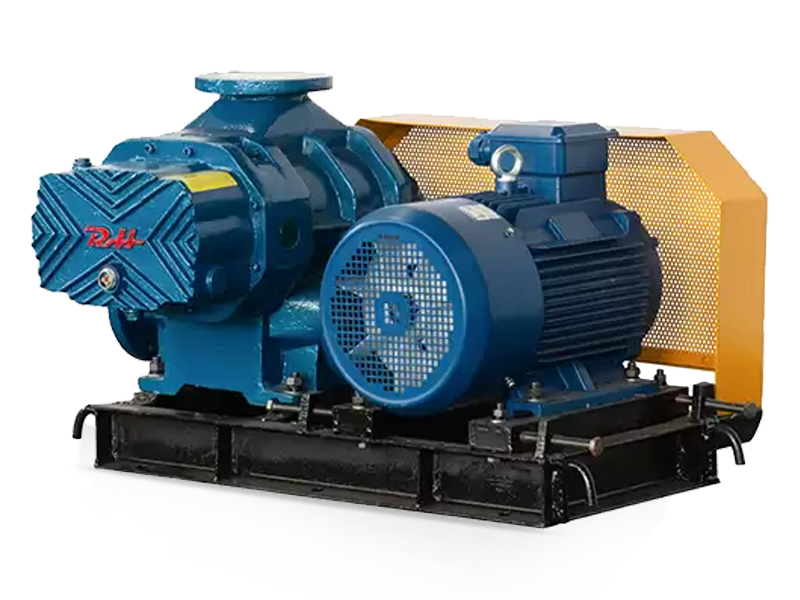
Choosing the appropriate Roots blower requires careful consideration of several factors, including required airflow rate, operating pressure, gas type, and environmental conditions. Engineers must also account for efficiency curves, noise levels, and maintenance accessibility. Using blowers with variable speed drives can improve energy efficiency by matching output to process demand. A proper selection ensures reliable performance, energy savings, and reduced maintenance costs.
Key Selection Parameters
- Airflow capacity (m³/h or CFM) to meet process requirements
- Operating pressure range to avoid overloading
- Gas composition, including moisture or dust content
- Temperature limits for continuous operation
- Energy efficiency and potential for variable speed operation
Energy Efficiency and Modern Innovations
Modern Roots blowers are designed to reduce energy consumption while maintaining high reliability. The integration of variable frequency drives (VFDs) allows for precise airflow control and lower energy usage during partial-load operations. Advanced materials for lobes and casing reduce friction and wear, extending service intervals. Additionally, soundproofing technologies and pulse-damping designs improve operational safety and workplace comfort.
Conclusion
Roots blowers are indispensable in many industrial applications due to their simple yet effective design, reliability, and versatility. Proper understanding of their operating principles, maintenance requirements, and selection criteria ensures efficient, long-term performance. By leveraging modern innovations such as VFDs and improved materials, industries can achieve higher energy efficiency, lower operational costs, and consistent process outcomes.


 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى