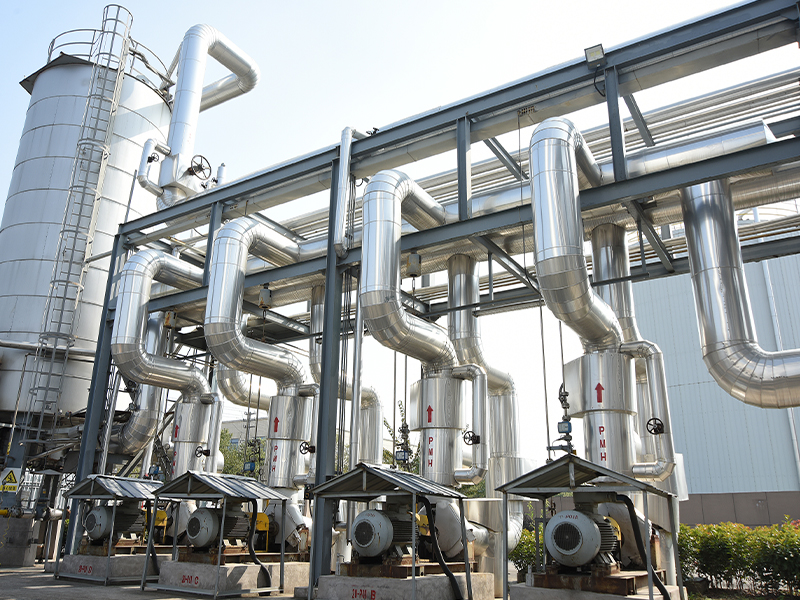
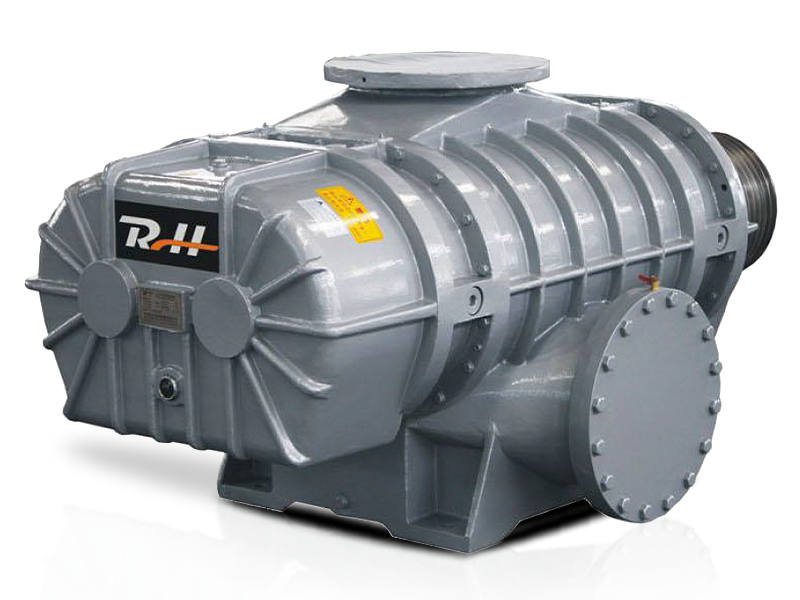
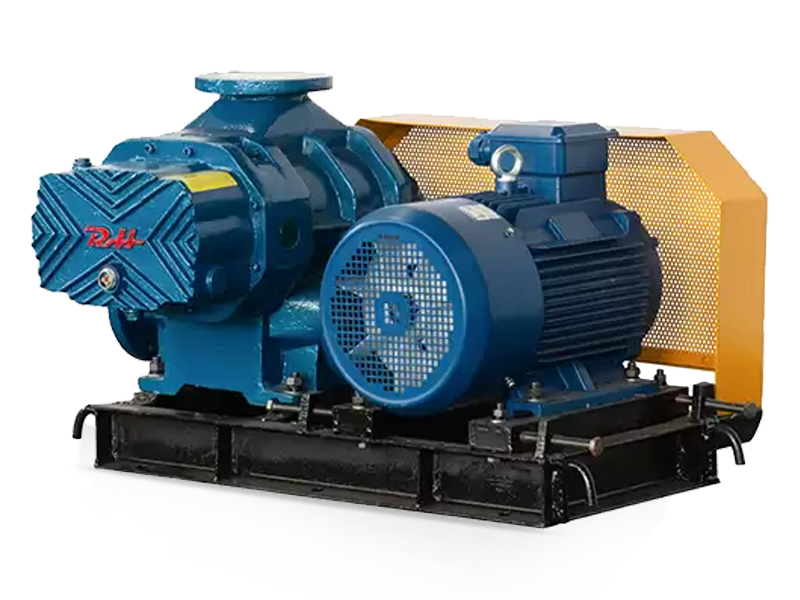
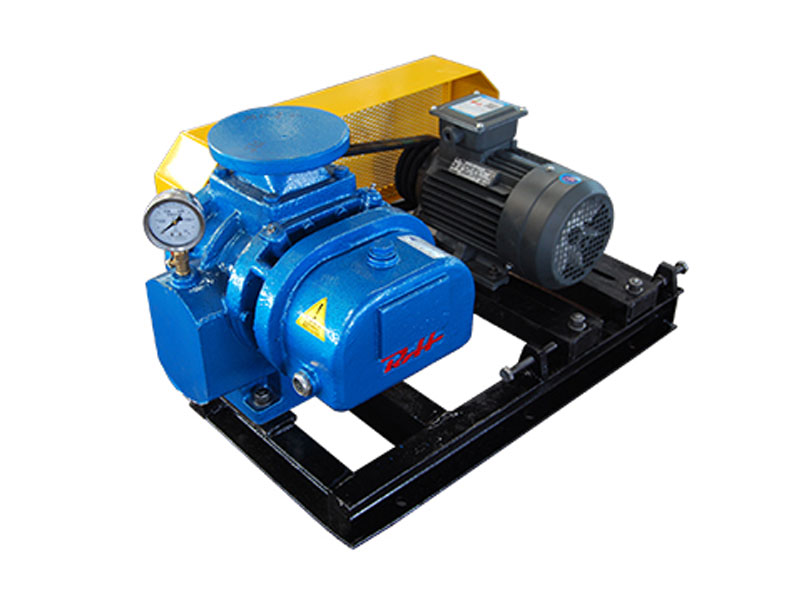
Oil-free screw blowers are widely recognized for their reliability, clean operation, and low maintenance in compressed air systems. While they are commonly used for delivering high volumes of clean air or gas in industrial processes, a common question arises: can oil-free screw blowers be used in vacuum applications?
Understanding Oil-Free Screw Blowers
Oil-free screw blowers are a type of rotary positive displacement machine. They use two intermeshing rotors to compress and move air or gas without any lubricating oil coming into contact with the airflow. This design ensures the air or gas remains clean and uncontaminated, making oil-free screw blowers particularly suitable for industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and electronics manufacturing.
Key characteristics of oil-free screw blowers include:
- Clean operation: No oil in the compression chamber means zero risk of contamination.
- Durability: Designed for continuous operation under varying loads.
- Efficiency: Capable of maintaining stable flow rates under moderate pressure variations.
These properties make them attractive for processes that require both reliability and purity.
Oil-Free Screw Blowers vs. Vacuum Pumps
To determine whether oil-free screw blowers are suitable for vacuum applications, it’s essential to understand the difference between blowers and vacuum pumps.
- Blowers are designed primarily to move air or gas from a lower pressure region to a higher pressure region. They create positive pressure, typically ranging from 0.5 to 2 bar above atmospheric pressure.
- Vacuum pumps are designed to remove air or gas from a chamber, reducing the pressure below atmospheric levels. They create negative pressure (vacuum), measured in terms of millibar or inches of mercury.
The fundamental design of oil-free screw blowers is for positive pressure applications. However, some blowers can operate in low vacuum or suction conditions, depending on the design and control system. They are not typically designed for high or deep vacuum applications, where specialized vacuum pumps like rotary vane, diaphragm, or liquid-ring pumps are more suitable.
Technical Considerations for Vacuum Applications
-
Vacuum Level Requirements:
Oil-free screw blowers can generate mild vacuum levels, generally up to 0.5 bar below atmospheric pressure. For applications requiring high vacuum (e.g., below 10 mbar), a dedicated vacuum pump is necessary. -
Airflow and Pressure Control:
In vacuum operation, the blower must handle reverse flow conditions, where the system’s pressure is lower than the ambient. Using variable frequency drives (VFDs) can help regulate the blower speed and prevent mechanical stress under such conditions. -
Sealing and Leakage:
Since screw blowers are designed for positive pressure, internal clearances are optimized to minimize air leakage at higher pressures. At vacuum, these clearances can lead to reduced efficiency, as some air may leak back into the rotor chamber. Proper system sealing is crucial to maintain performance. -
Temperature Considerations:
Air or gas compression generates heat in positive-pressure operation. In vacuum mode, while heat generation is lower, care must be taken to prevent condensation or temperature fluctuations that could affect performance or system components.

Practical Applications
Despite the limitations, oil-free screw blowers are successfully used in low to medium vacuum applications across multiple industries:
- Pneumatic Conveying: For moving powders or granules where moderate vacuum is sufficient to transport materials.
- Aeration in Wastewater Treatment: Blowers can create slight vacuum to draw air into diffusers.
- Packaging and Suction Systems: Oil-free blowers are used in vacuum packaging machines for food or pharmaceuticals.
- Medical and Laboratory Equipment: Certain clean-air applications utilize blowers for negative pressure without introducing contaminants.
These examples demonstrate that with proper system design, oil-free screw blowers can meet vacuum requirements in scenarios that do not demand deep vacuum levels.
Advantages of Using Oil-Free Screw Blowers in Vacuum Applications
- Clean Air: The absence of oil ensures that sensitive processes remain contamination-free.
- Low Maintenance: Oil-free operation reduces the need for frequent servicing compared to oil-lubricated vacuum pumps.
- Durability: Designed for continuous operation, screw blowers can maintain moderate vacuum reliably.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern blowers with VFDs can adjust airflow and pressure to match system demand, reducing energy consumption.
Limitations and Precautions
While oil-free screw blowers can be adapted for certain vacuum applications, there are notable limitations:
- Limited Vacuum Depth: They are not suitable for high or ultra-high vacuum applications.
- Reduced Efficiency: Vacuum operation may lead to leakage and lower efficiency compared to dedicated vacuum pumps.
- Installation Considerations: Systems may require additional accessories such as check valves, pressure sensors, or VFDs to operate effectively under vacuum.
- Noise and Vibration: Operating outside typical design parameters can increase noise or vibration, requiring monitoring and mitigation.
Conclusion
Oil-free screw blowers can be used in vacuum applications, but mainly for low to moderate vacuum levels. Their clean operation, reliability, and low maintenance make them a valuable choice in industries where air purity is essential. However, for applications requiring deep vacuum, specialized vacuum pumps are still the preferred option. Proper system design, including airflow control, sealing, and monitoring, is essential to ensure that the blower operates efficiently and safely under vacuum conditions.
In summary, oil-free screw blowers are versatile machines that, when correctly applied, can support a range of vacuum operations while maintaining the advantages of oil-free technology. Understanding their limitations and tailoring the system accordingly will help engineers and operators achieve optimal performance without compromising reliability or air quality.


 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى