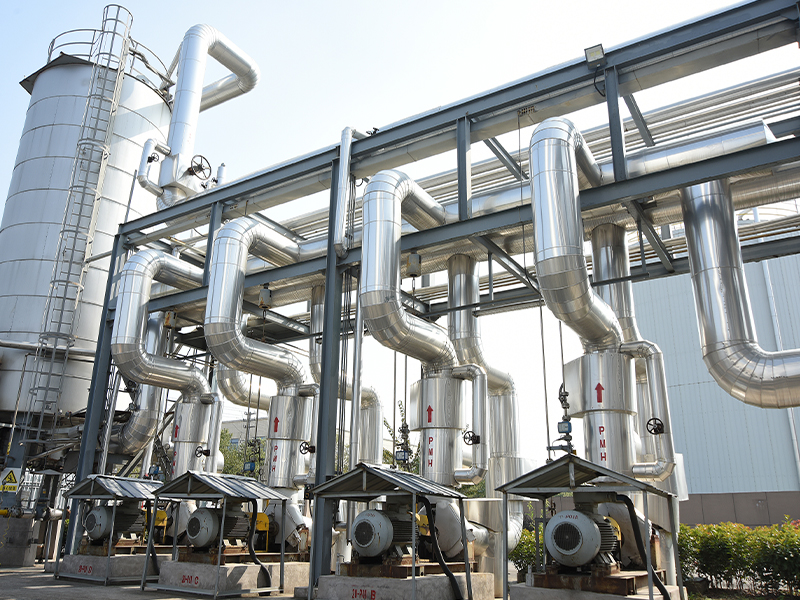
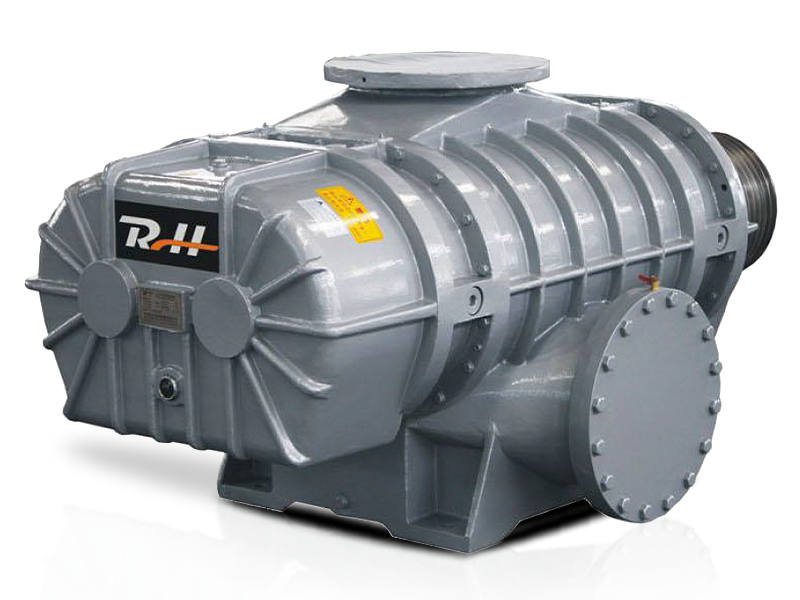
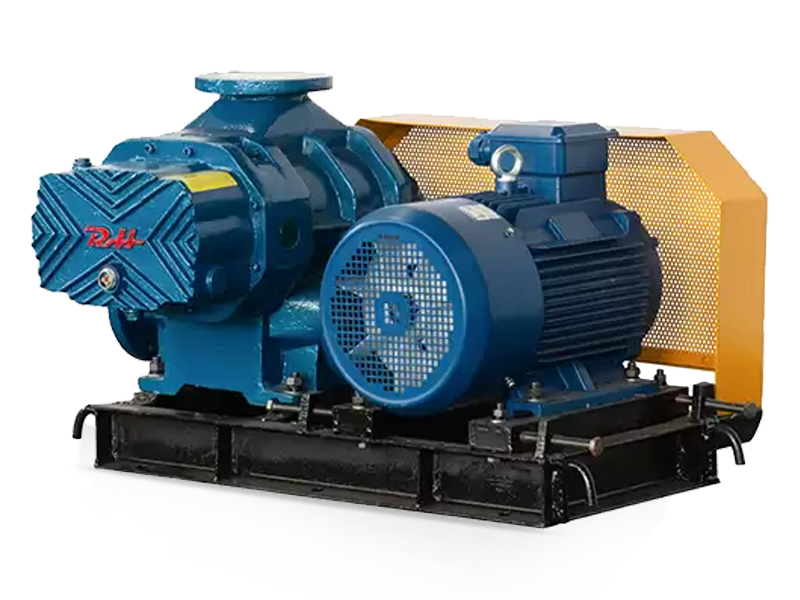
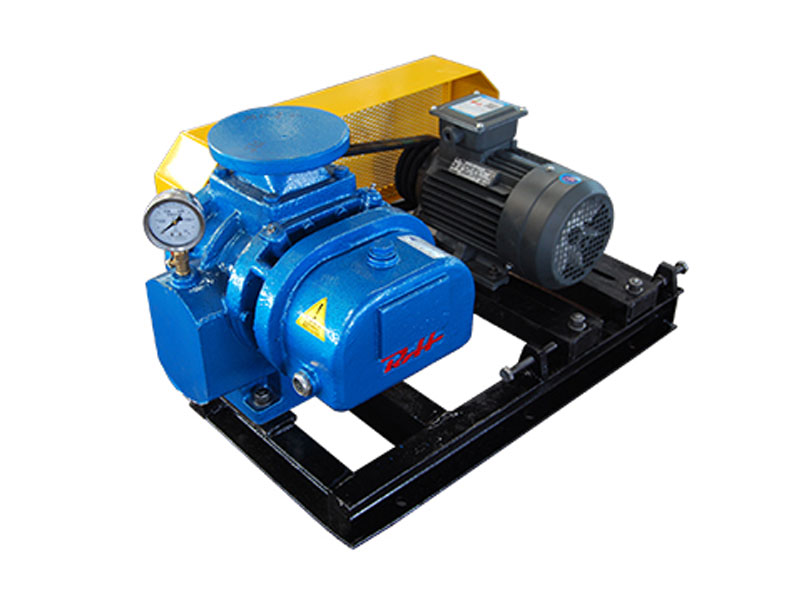
Rotary blower, also known as rotary lobe blowers or positive displacement blowers, are essential machines in various industrial applications. They provide efficient air movement with consistent flow rates, making them ideal for pneumatic conveying, wastewater treatment, and more. This guide explains everything you need to know about rotary blower technology, maintenance, and selection.
How Rotary Blowers Work: Basic Principles
The fundamental operation of a rotary blower involves two rotating lobes (or screws) that trap air between the rotor and casing, then push it through the discharge port. Unlike centrifugal blowers that use impellers, rotary blowers provide constant airflow regardless of pressure changes, making them perfect for applications requiring steady air supply.
Key Components of Rotary Lobe Blowers
Understanding these critical parts will help with maintenance and troubleshooting:
- Rotors/Lobes: Typically two or three-lobe designs that rotate in opposite directions
- Housing/Casing: Contains the rotors and maintains pressure
- Inlet and Outlet Ports: For air intake and discharge
- Timing Gears: Synchronize rotor movement
- Bearings: Support rotor shafts
- Seals: Prevent air leakage
Types of Rotary Blowers Compared
| Type | Pressure Range | Flow Rate | Efficiency | Best Applications |
| Two-Lobe Blowers | Up to 15 psi | Medium-High | Good | Wastewater treatment, pneumatic conveying |
| Three-Lobe Blowers | Up to 15 psi | High | Better | Industrial processes requiring smoother flow |
| Helical Screw Blowers | Up to 30 psi | Medium | Best | Higher pressure applications, energy-sensitive uses |
Rotary Blower vs. Other Air Movement Technologies
When selecting between air movement technologies, consider these key differences:
| Feature | Rotary Blower | Centrifugal Blower | Roots Blower | Regenerative Blower |
| Pressure Capability | Medium (up to 15-30 psi) | Low-Medium | Low-Medium | Very Low |
| Flow Consistency | Constant | Variable | Constant | Variable |
| Energy Efficiency | Good at design point | Good across range | Fair | Poor |
| Maintenance Needs | Moderate | Low | High | Very Low |
Top Applications for Industrial Rotary Blowers
These machines serve critical functions across multiple industries:
Wastewater Treatment Plants
Rotary blowers provide the aeration needed for biological treatment processes. Their ability to deliver constant airflow makes them ideal for maintaining proper oxygen levels in treatment tanks.
Pneumatic Conveying Systems
In manufacturing and processing plants, rotary blowers move powders, granules, and other dry materials through pipelines without contamination.
Industrial Vacuum Systems
Many central vacuum systems in factories use rotary blowers to generate the vacuum needed for material handling and cleaning.
Aquaculture Operations
Fish farms and hatcheries use rotary blowers to oxygenate water in ponds and tanks, ensuring healthy aquatic environments.
Energy Efficiency in Rotary Blower Systems
Modern rotary blowers can achieve significant energy savings through:
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): Adjust motor speed to match demand
- Improved Rotor Designs: Three-lobe and helical screw configurations reduce energy losses
- Precision Manufacturing: Tighter tolerances minimize air leakage
- Heat Recovery Systems: Capture waste heat for other processes
Maintenance Guide for Rotary Lobe Blowers
Proper maintenance extends equipment life and prevents costly downtime:
Daily Checks
- Monitor vibration levels
- Check for unusual noises
- Verify proper oil levels (if oil-lubricated)
- Inspect for air leaks
Monthly Maintenance
- Inspect and clean filters
- Check belt tension (if belt-driven)
- Monitor bearing temperatures
- Verify proper alignment
Annual Service
- Replace worn seals
- Inspect and regrease bearings
- Check rotor clearances
- Test safety systems
Troubleshooting Common Rotary Blower Problems
| Problem | Possible Causes | Solutions |
| Excessive Vibration | Imbalance, misalignment, worn bearings | Balance rotors, realign components, replace bearings |
| Overheating | Blocked filters, high discharge pressure, lubrication issues | Clean/replace filters, check system pressure, verify proper lubrication |
| Reduced Airflow | Worn rotors, leaking seals, clogged intake | Inspect and replace worn components, clean intake |
| Unusual Noises | Rotor contact, bearing failure, gear wear | Check clearances, inspect bearings and gears |
Selecting the Right Rotary Blower for Your Application
Consider these factors when choosing a rotary blower:
Flow Rate Requirements
Calculate your required CFM (cubic feet per minute) based on process needs. Rotary blowers typically range from 50 to 5,000 CFM.
Pressure Needs
Determine both working pressure and any pressure peaks in your system. Most rotary blowers operate between 7-15 psi.
Duty Cycle
Continuous operation requires more robust construction than intermittent use applications.
Environmental Conditions
Consider ambient temperature, humidity, and potential contaminants that could affect performance.
Advantages of Rotary Blower Technology
- Constant Airflow: Delivers steady flow regardless of pressure changes
- Oil-Free Operation: Many models don't require lubricants in the air stream
- Durability: Simple design with few moving parts ensures long service life
- Low Maintenance: Compared to other positive displacement technologies
- Versatility: Handles various gases and operates in multiple orientations
Limitations of Rotary Blowers
While highly effective for many applications, rotary blowers have some constraints:
- Limited to medium pressure ranges (typically below 30 psi)
- Can be noisy at higher speeds and pressures
- Pulsation in two-lobe designs may require dampeners
- Not as energy efficient as some alternatives at partial loads
Future Trends in Rotary Blower Technology
The industry continues to evolve with several promising developments:
Improved Energy Efficiency
New rotor profiles and bearing technologies are reducing power consumption by 10-15% in latest models.
Smart Monitoring Systems
IoT-enabled sensors allow real-time performance tracking and predictive maintenance.
Advanced Materials
Composite rotors and specialized coatings are extending service intervals and durability.
Noise Reduction
Innovative housing designs and acoustic treatments are making blowers quieter.
Frequently Asked Questions About Rotary Blowers
How long do rotary blowers typically last?
With proper maintenance, rotary blowers can operate for 50,000-100,000 hours before major overhaul. Key factors affecting lifespan include operating conditions, maintenance practices, and load profile.
Can rotary blowers handle wet air or moisture?
While they can tolerate some moisture, excessive liquid can cause damage. Special coatings and drainage options are available for humid environments.
What's the difference between rotary blowers and compressors?
Blowers typically operate at lower pressures (below 30 psi) with higher flow rates, while compressors achieve higher pressures with reduced flows.
How often should rotary blower oil be changed?
For oil-lubricated models, typically every 2,000-8,000 operating hours depending on service conditions and manufacturer recommendations.
Conclusion: Rotary Blowers as Reliable Workhorses
Rotary blowers remain one of the most dependable solutions for industrial air movement needs. Their simple yet effective design delivers consistent performance across countless applications. By understanding the principles outlined in this guide - from selection criteria to maintenance best practices - you can ensure optimal performance and longevity from your rotary blower systems.
Whether you're specifying new equipment or maintaining existing installations, the combination of proper sizing, routine care, and timely troubleshooting will maximize your return on investment in this critical technology.


 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى