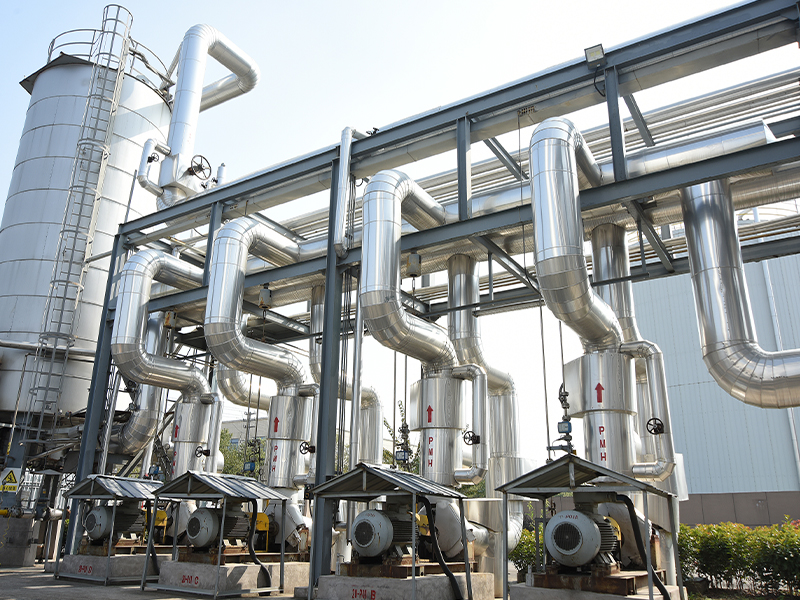
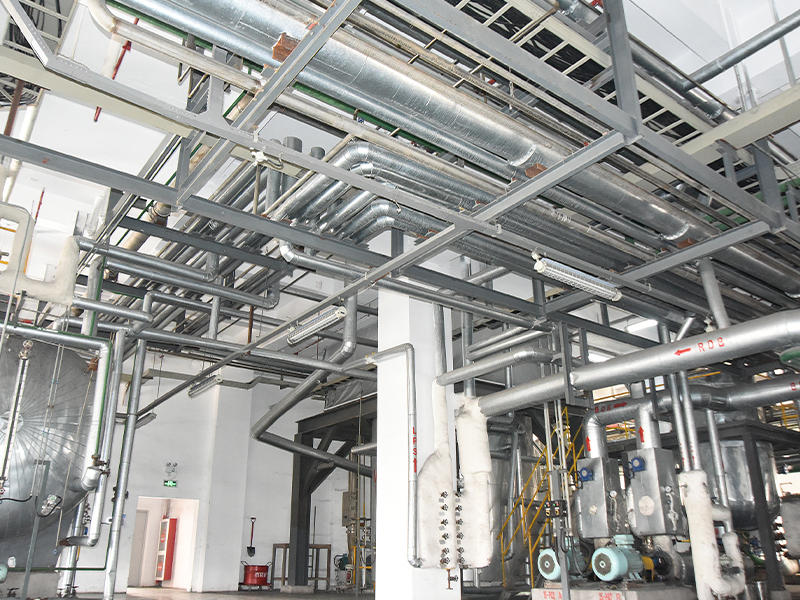
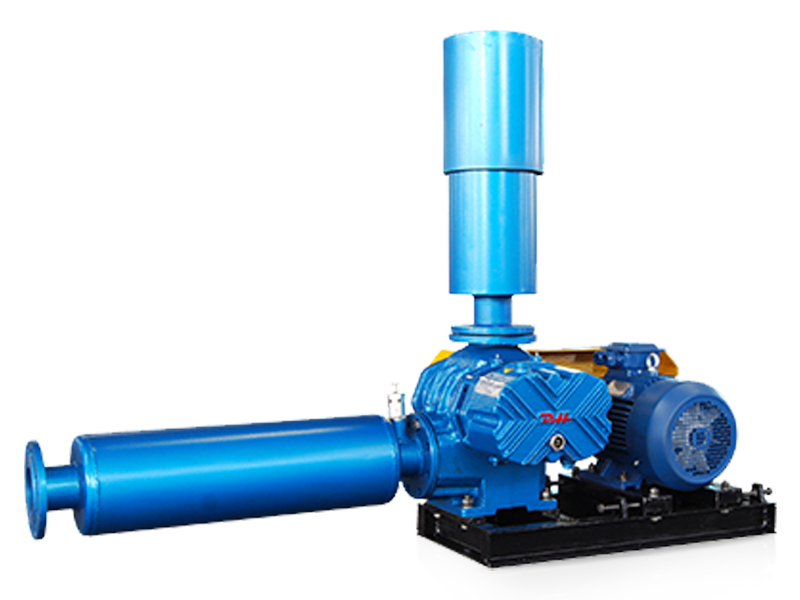
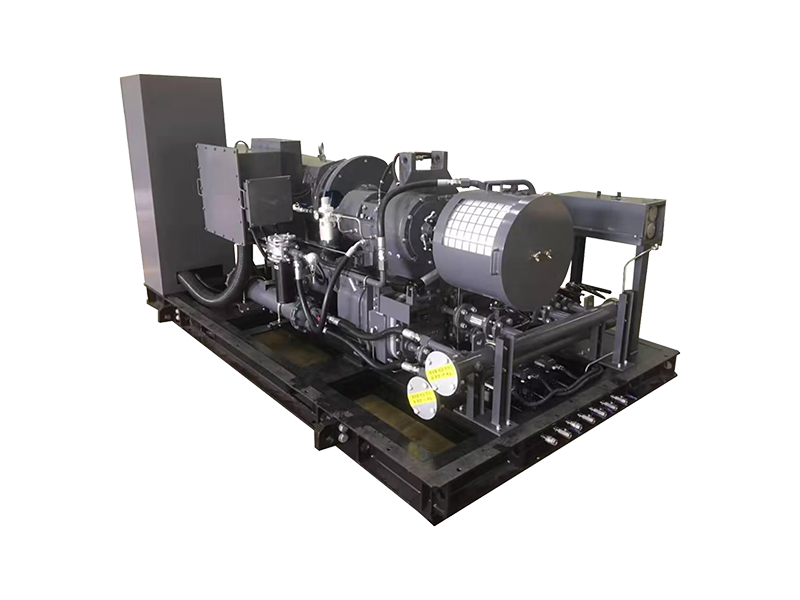
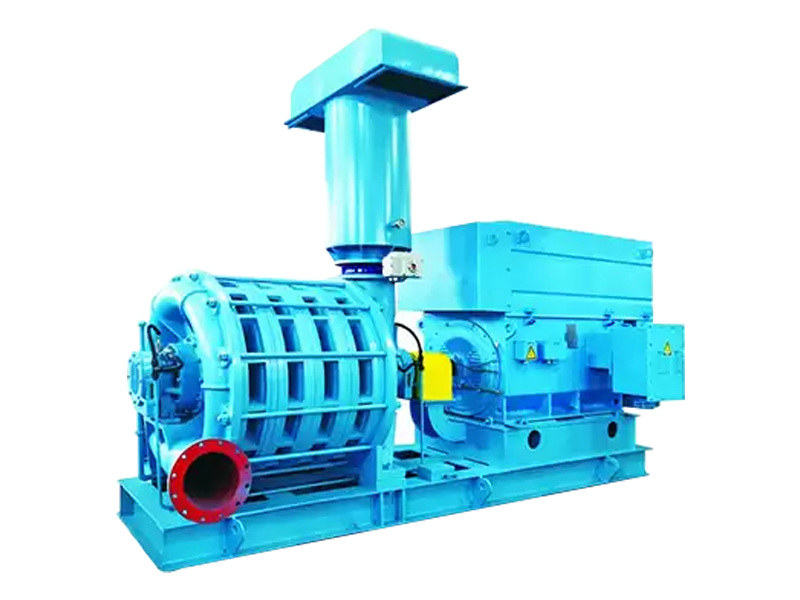
In the realm of industrial material handling, pneumatic conveying systems have gained significant prominence due to their efficiency, flexibility, and ability to handle a wide range of materials. At the heart of many pneumatic conveying systems lies the roots blower, a reliable and versatile device that plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth and efficient transfer of materials. This article delves into the working principles, design features, applications, and advantages of pneumatic conveying roots blowers, shedding light on their importance in modern industrial processes.
Working Principles of Roots Blowers
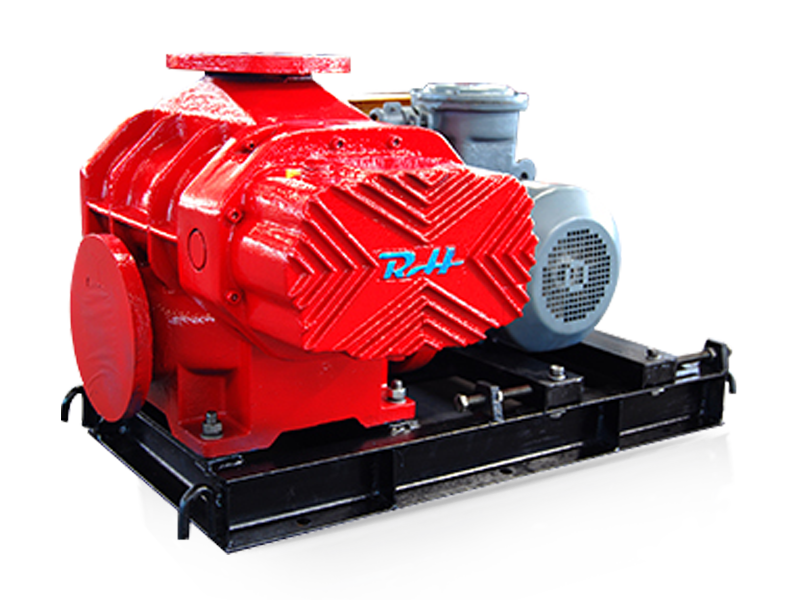
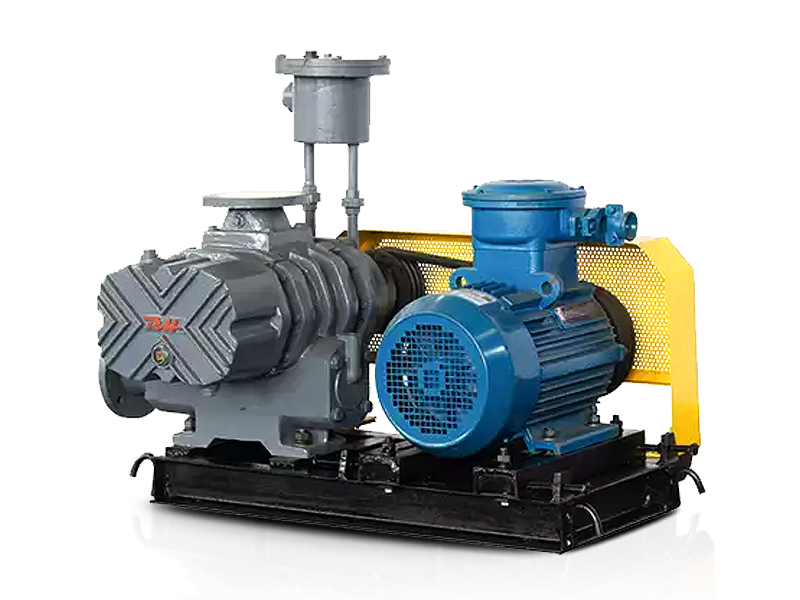
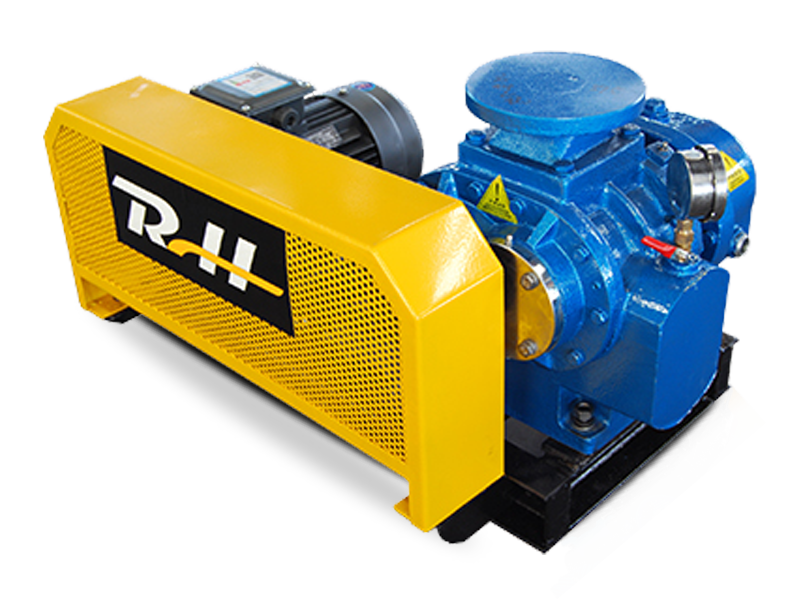
Roots blowers operate on the principle of positive displacement. They consist of two or more rotors, typically with lobes, that rotate in opposite directions within a closely fitted casing. As the rotors turn, they trap pockets of air or gas between the lobes and the casing walls. These pockets are then carried from the inlet side of the blower to the outlet side, where they are discharged. The continuous rotation of the rotors creates a steady flow of air or gas, which is used to transport materials in pneumatic conveying systems.
The key to the roots blower's operation is the precise clearance between the rotors and the casing. This clearance is designed to be small enough to minimize leakage but large enough to prevent the rotors from coming into contact with each other or the casing. The use of high-quality bearings and seals helps to maintain this clearance and ensure smooth operation over an extended period.
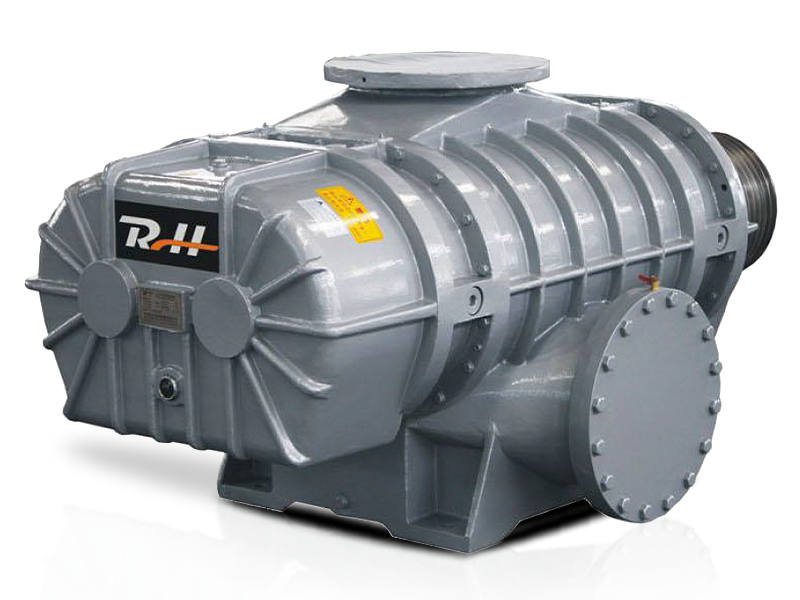
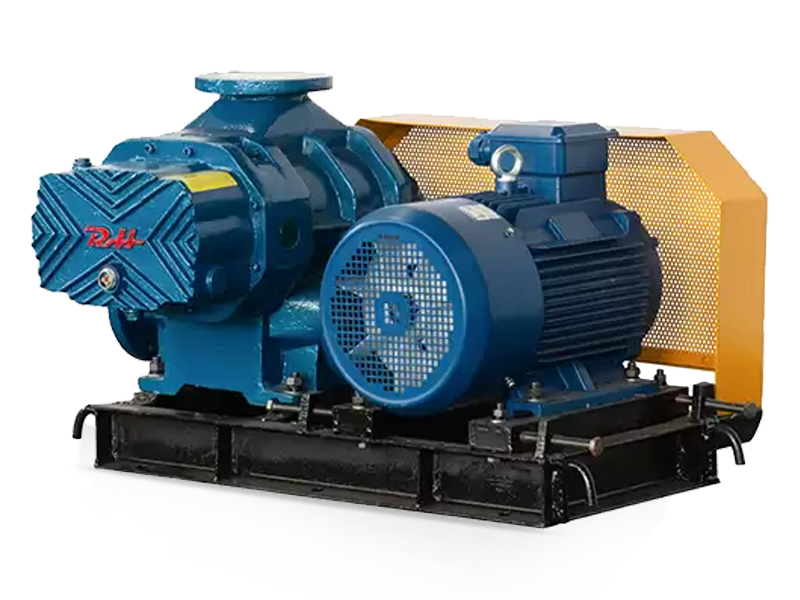
Design Features of Pneumatic Conveying Roots Blower
Rotor Design
The design of the rotors is a critical factor in the performance of a roots blower. Modern roots blowers often feature three-lobe rotors, which offer several advantages over traditional two-lobe designs. Three-lobe rotors provide a more balanced and efficient operation, resulting in reduced vibration and noise levels. They also offer a larger displacement volume per revolution, allowing for higher flow rates and greater efficiency.
Casing and Housing
The casing and housing of a roots blower are typically made from cast iron or steel to provide strength and durability. The internal surfaces of the casing are precision-machined to ensure a close fit with the rotors, minimizing leakage and maximizing efficiency. Some roots blowers are also equipped with soundproof enclosures to reduce noise emissions, making them suitable for use in environments where noise control is a concern.
Sealing and Lubrication
To prevent leakage and ensure smooth operation, roots blowers are equipped with high-quality seals and lubrication systems. Seals are used to prevent air or gas from escaping between the rotors and the casing, as well as between the blower and the connected piping. Lubrication systems, on the other hand, are used to reduce friction and wear between the moving parts of the blower, extending its lifespan and improving its performance.
Applications of Pneumatic Conveying Roots Blowers
Pneumatic conveying roots blowers find applications in a wide range of industries, including:
Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage industry, roots blowers are used to transport a variety of materials, such as flour, sugar, grains, and powders. They are also used in the production of carbonated beverages, where they help to maintain the proper pressure and flow of carbon dioxide.
Chemical Industry
The chemical industry relies on roots blowers for the transportation of chemicals, powders, and granules. They are used in processes such as mixing, blending, and packaging, as well as in the transfer of materials between different stages of production.
Pharmaceutical Industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, roots blowers are used to transport sensitive materials, such as drugs and powders, in a controlled and contamination-free environment. They are also used in the production of medical gases, such as oxygen and nitrogen.
Cement and Building Materials Industry
The cement and building materials industry uses roots blowers to transport materials such as cement, sand, gravel, and fly ash. They are an essential component in the production of concrete, bricks, and other building materials.
Power Generation Industry
In the power generation industry, roots blowers are used to transport coal, ash, and other materials in power plants. They are also used in the production of biomass energy, where they help to transport biomass materials to the combustion chamber.
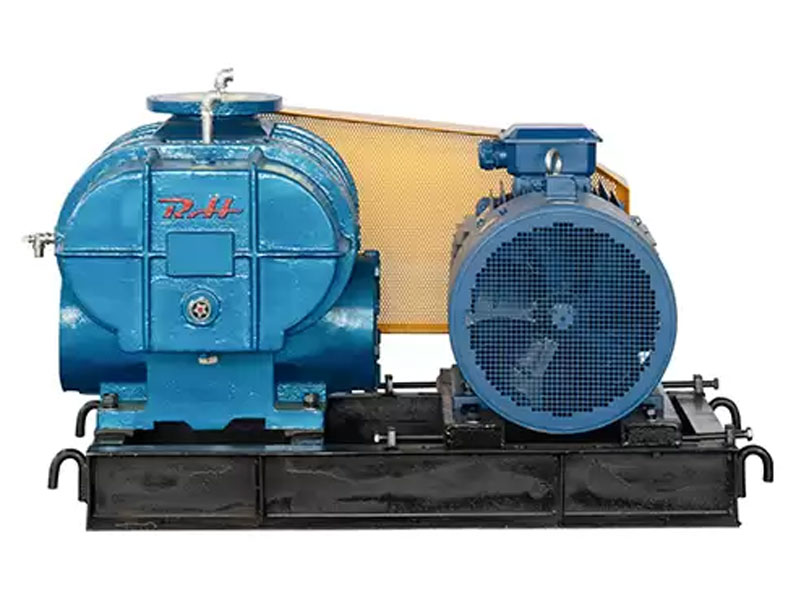

Advantages of Pneumatic Conveying Roots Blowers
High Efficiency
Roots blowers are known for their high efficiency in pneumatic conveying applications. They are able to provide a steady and reliable flow of air or gas, ensuring the efficient transportation of materials over long distances. Their positive displacement design allows them to maintain a constant flow rate, even under varying pressure conditions.
Versatility
Pneumatic conveying roots blowers are highly versatile and can be used to transport a wide range of materials, including powders, granules, and small particles. They can be easily adapted to different conveying systems and can be configured to operate at different pressures and flow rates.
Low Maintenance
Roots blowers are relatively simple in design and have few moving parts, making them easy to maintain. They require regular lubrication and inspection of the seals and bearings, but overall, they have a long lifespan and are highly reliable.
Cost-Effective
Compared to other types of blowers and conveying systems, roots blowers are often more cost-effective. They are relatively inexpensive to purchase and operate, and their low maintenance requirements help to reduce overall operating costs.
Conclusion
Pneumatic conveying roots blowers are an essential component in modern industrial material handling systems. Their reliable performance, high efficiency, versatility, and cost-effectiveness make them a popular choice for a wide range of applications across various industries. As technology continues to advance, roots blowers are likely to become even more efficient and reliable, further enhancing their importance in the world of industrial material handling.


 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى